在后执行脚本中:
function formatDate(date, fmt) {
let o = {
'M+': date.getMonth() + 1, //月份
'd+': date.getDate(), //日
'h+': date.getHours(), //小时
'm+': date.getMinutes(), //分
's+': date.getSeconds(), //秒
"q+": Math.floor((date.getMonth() + 3) / 3), //季度
"S": date.getMilliseconds() //毫秒
};
if (/(y+)/.test(fmt)) { //年份
fmt = fmt.replace(RegExp.$1, (date.getFullYear() + '').substr(4 - RegExp.$1.length));
}
for (let k in o) {
if (new RegExp("(" + k + ")").test(fmt)) {
let str = o[k] + '';
fmt = fmt.replace(RegExp.$1, (RegExp.$1.length === 1) ? str : padLeftZero(str));
}
}
return fmt;
};
function padLeftZero(str) {
return ('00' + str).substr(str.length);
}
console.log(JSON.parse(response.json.put).时间戳);
let 时间戳 = JSON.parse(response.json.put).时间戳;
let date = new Date(时间戳); //此为时间戳
console.log(formatDate(date, 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm'));
将获取的变量设置成环境中,在body中直接写成变量的形式即可
apt.environment.set("时间戳", formatDate(date, 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm'));
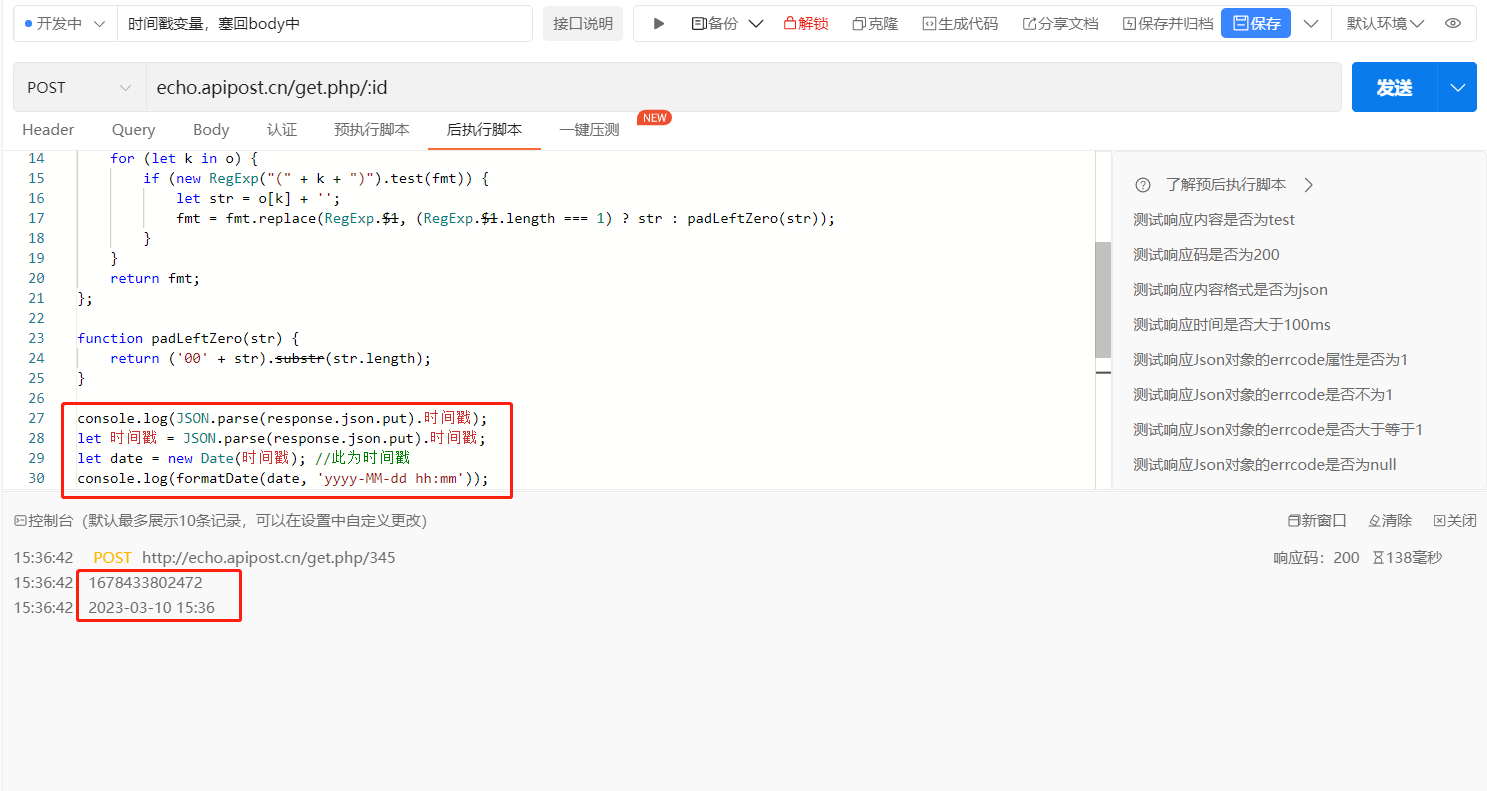
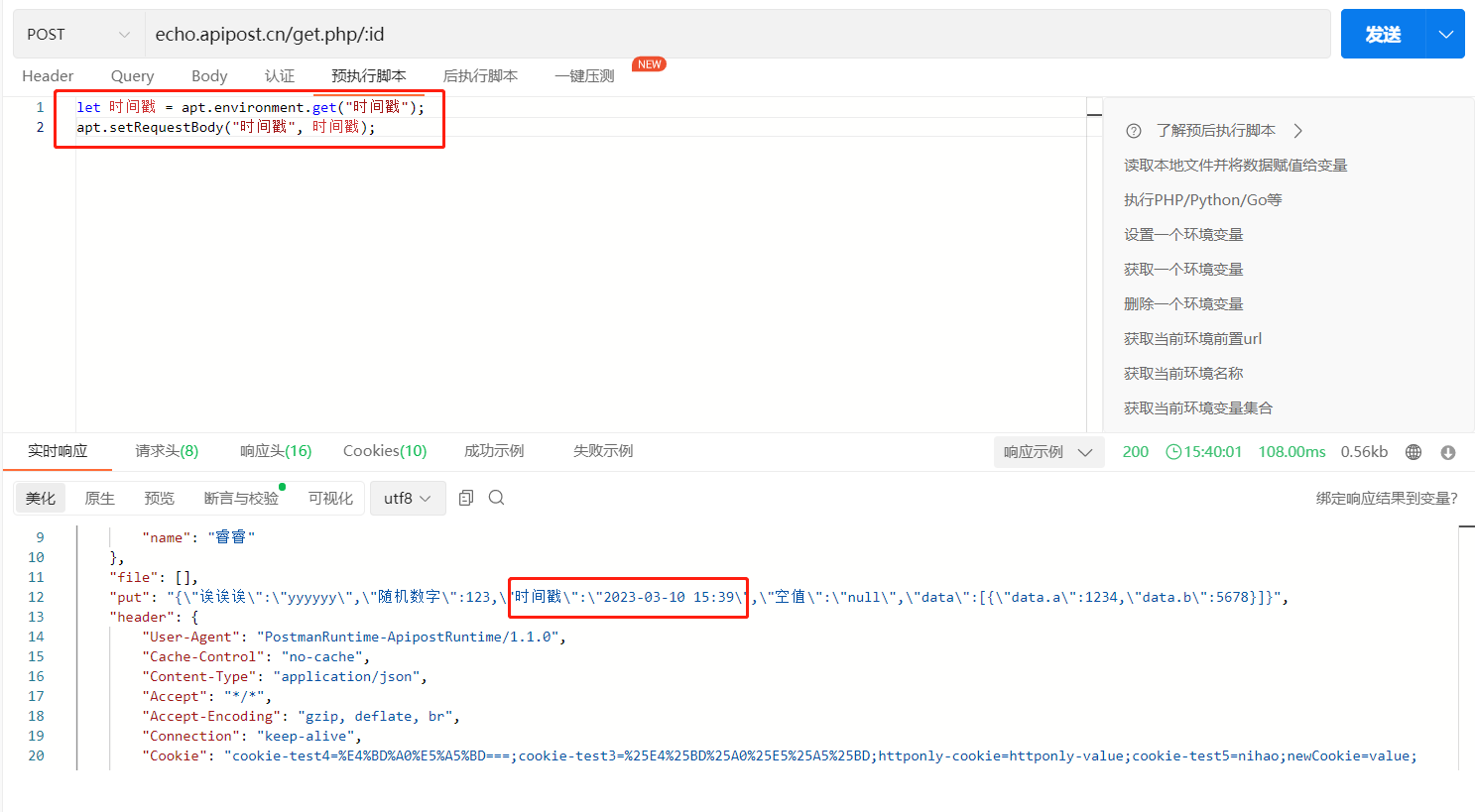
然后在预执行脚本中,获取后执行脚本中设置的环境时间戳变量,并塞回到body中,
这样我们就利用时间戳,直接拿到转换的当前时间啦!
更多Apipost使用小知识小技巧,请在官网首页扫码加入我们技术交流群吧~~