 宅哥聊构架 后端
2025-01-07
宅哥聊构架 后端
2025-01-07

Java程序员和Spring息息相关,Spring在为广大Java程序员提供了极大的便捷性的同时也带来了极多的配置文件,SpringBoot在这样的环境下应运而生,它以约定大于配置的方式让Java程序员在繁杂的配置文件中脱离出来,让Java程序员只用按需引入各种Starter并加载默认配置,几乎做到开箱即用,SpringBoot能提供这样的能力依赖于它的自动配置模式,接下来就简单下SpringBoot自动配置以及自己动手实现一个SpringBoot Starter并在其中介绍一些小技巧。
一个简单的SpringBoot如下:java
代码解读复制代码@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
其中最主要的就是@SpringBootApplication注解,那么它有什么神奇之处呢,我们进入@SpringBootApplication注解可以看到java
代码解读复制代码@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
@SpringBootApplication其实是一个复合注解包括@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan,我们今天主要讨论到是自动配置,所以望文生义肯定与@EnableAutoConfiguration注解息息相关,我们继续进入@EnableAutoConfiguration注解java
代码解读复制代码@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
我们可以看到@AutoConfigurationPackage和@Import,@Import注解的主要功能就是将Class导入到IOC容器中,接下来我们就介绍一下@EnableAutoConfiguration注解实现的两个功能
@AutoConfigurationPackagejava
代码解读复制代码@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
@AutoConfigurationPackage 利用@Import注解把AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class导入到IOC容器,AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class主要的功能就是扫描主类所在包及其子包以及basePackages和basePackageClasses配置的包及其子包下的Bean加入IOC容器,里面的代码相对简单,感兴趣的小伙伴可以打开源代码看一看
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)将AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class导入IOC容器,AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class里面有个方法java
代码解读复制代码protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
看方法也能大致知道它的功能是获取自动配置的Entry,其中主要的方法是getCandidateConfigurations,我们继续进入java
代码解读复制代码protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
其实在这通过方法中的Assert提示消息
No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.
也能推测出SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法是通过META-INF/spring.factories文件查找auto configuration classes,我们继续进入SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法java
代码解读复制代码public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
在方法尾部loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse)返回了一个Map然后通过factoryTypeName获取了value,而factoryTypeName的值在此时正是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration,我们继续进入loadSpringFactories方法java
代码解读复制代码private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
//FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION="META-INF/spring.factories"
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
...
}
可以看到根据常量FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION扫描jar路径下的所有URL,而FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的值是等于META-INF/spring.factories的,所以该方法是将jar路径下的所有META-INF/spring.factories配置文件读取到Map对象中,再通过key=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration获取到value也就是需要自动配置的Class
关于自动配置的部分就讲完了,下面我们介绍如何自定义一个SpringBoot Starter
SpringBoot Starter首先新建一个SpringBoot Maven项目,比较简单这里就不多做讲解了,需要注意的点是artifactId通常为xxx-spring-boot-starter,因为官方提供的starter以spring-boot-starter-xxx命名,所以官方建议自定义的starter用xxx-spring-boot-starter命名与官方做一个区分的同时也保持一定的命名规范,当然如果只是公司内部或者个人的一些组件或工具也可以用xxx-component或其他名字来命名,这里想表达的意思是在团队协作中最好保持一定的命名规范,让团队其他成员减少不必要的理解成本或歧义。
代码结构如下:
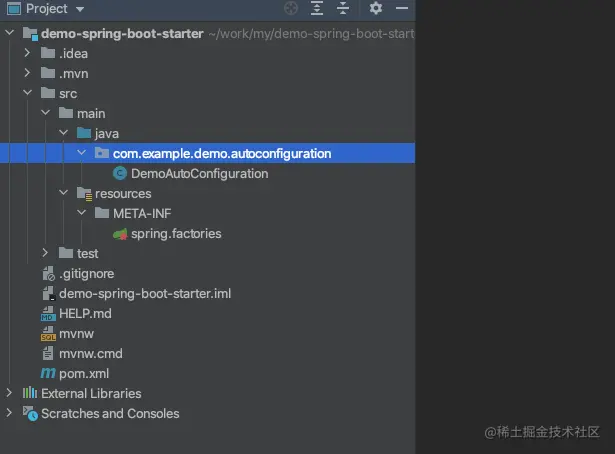
根据上面讲的自动配置流程,我们需要在resources目录下创建META-INF/spring.factories文件,同时新建自动配置类DemoAutoConfiguration.java,
spring.factories内容如下properties
代码解读复制代码org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.example.demo.autoconfiguration.DemoAutoConfiguration
上面讲过获取自动配置是以org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration为key所以我们需要这样配置,至此最简单的starter已经实现了,但是这个starter没提供任何能力,所以它是毫无意义的,我们接下来模拟一个发送邮件的功能来丰富我们的starter。
我们新增一个properties配置类java
代码解读复制代码@Getter
@Setter
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mail")
public class DemoProperties {
private String address;
private String msg;
}
修改DemoAutoConfiguration.javajava
代码解读复制代码@EnableConfigurationProperties({DemoProperties.class})
public class DemoAutoConfiguration {
}
关于@EnableConfigurationProperties可以查看我另一片文章,@EnableConfigurationProperties使用技巧
我们创建一个service,同时修改DemoAutoConfigurationjava
代码解读复制代码@AllArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class MailService {
private DemoProperties properties;
public void send(){
log.warn("mail address is {}, msg is {}", properties.getAddress(), properties.getMsg());
}
}java 代码解读复制代码@EnableConfigurationProperties({DemoProperties.class})
public class DemoAutoConfiguration {
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Bean
MailService mailService(DemoProperties properties){
return new MailService(properties);
}
}
可以发现,我们没有用@Service注解来标记MailService,而是在DemoAutoConfiguration里面手动的注册MailService为Bean,为什么要大费周章的自己手动注册呢?在这有个编码习惯,当你对外提供服务时,尽量让自己的服务处在可控制的状态,以防与用户预期产生差异性,在这只是一个很简单的例子,如果是一个非常复杂的模块或者Starter再与其他服务进行交互时这是非常有必要的,比如这个例子,只有当DemoAutoConfiguration被自动配置时MailService才会被IOC容器管理,如果采用@Service注解,用户刚好扫描到你的包,那即使你的自动配置是没启用的MailService也会被IOC容器管理,这在大部分时候可能没啥影响,但是积少成多你的系统将越来越不可控。
接下来我们执行mvn clean install这样一个新鲜的Starter就生成了,在另一个项目中引入该Starterjava
代码解读复制代码 <dependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
在application.yml中配置yaml
代码解读复制代码mail:
address: test@foxmail.com
msg: hello
在启动类类做个简单的测试typescript
代码解读复制代码@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
@Autowired
MailService mailService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@EventListener
public void ready(ApplicationReadyEvent event){
mailService.send();
}
}
启动项目可以得到消息
mail address is test@foxmail.com, msg is hello
至此SringBoot Starter简单示例就完成了,下面介绍一些小技巧,在大部分框架中会做一些开关,比如enabled配置,我们在properties中加入一个boolean类型的字段java
代码解读复制代码@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mail")
public class DemoProperties {
private boolean enabled;
private String address;
private String msg;
}
@ConditionalOnProperty在自动配置类上加入@ConditionalOnProperty注解,prefix表示前缀,value表示值的字段名,havingValue表示值为什么时生效,matchIfMissing表示默认值java
代码解读复制代码@EnableConfigurationProperties({DemoProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "mail", value = "enabled", havingValue="true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class DemoAutoConfiguration {
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Bean
MailService mailService(DemoProperties properties){
return new MailService(properties);
}
}
这样我们就可以通过配置控制我们的自动配置是否生效java
代码解读复制代码mail:
address: test@foxmail.com
msg: hello
enabled: false
如果现在改为false启动项目会报错,这是因为我们的自动配置设置为false后不会加载自动配置类,也就不会注入MailServicejava
代码解读复制代码Field mailService in com.example.demo.Application required a bean of type 'com.example.demo.service.MailService' that could not be found.
The injection point has the following annotations:
- @org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)
@Import
前面我们讲过@Import注解的作用,我们也可以利用@Import注解也实现自动配置的控制,创建注解@EnableMail,只做一件事就是引入自动配置类less
代码解读复制代码@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Import({DemoAutoConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableMail {
}
删除spring.factories的配置,然后重新install Starter,在测试项目中加入注解@EnableMailjava
代码解读复制代码@SpringBootApplication
@EnableMail
public class Application {
@Autowired
MailService mailService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@EventListener
public void ready(ApplicationReadyEvent event){
mailService.send();
}
}
启动项目,同样能得到下面的消息,这也是部分框架采用的自动配置的方式java
代码解读复制代码mail address is test@foxmail.com, msg is hello
依赖java
代码解读复制代码<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>